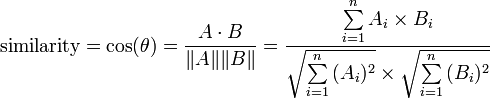我最近在调整我们网站GuruDigger 的类似文章推荐功能。
原先的类似文章推荐是基于用户自己打的标签,而标签大家往往打得比较随意,推荐的内容比较少,
我需要采用更好的方式来处理这个问题。
整体思路
推荐文章可以用协同过滤(Collaborative Filtering ),
不过要业务逻辑符合这个模式,以及数据量足够大才行,我还是用基于文章内容(Content Based)的算法来解决。
具体思路:
首先是分词。文章需要拆分成单元为词的串,然后才有办法处理。
然后从词串中获取能够代表文章内容意思的关键词。
然后基于文章的关键词,来选择类似的文章。
这种方法,文章数据只被利用到了词和词出现频率的信息,
另外也可以通过基于语义的方式来分析出更多内容,
对应的学术领域叫做Topic Modeling ,
我现在这个思路算是一个很简单的方法。
分词
采用mmseg 的分词方法。原理看起来比较简单,大家可以稍微了解一下。
具体实现采用的库是针对ruby的绑定rmmseg-cpp 。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
require 'rmmseg'
RMMSeg :: Dictionary . load_dictionaries
def cn_word_split text
algor = RMMSeg :: Algorithm . new ( text )
out = []
while tok = algor . next_token
out << to_utf8 ( tok . text )
end
out
end
def to_utf8 text
String . new ( text ) . force_encoding ( 'utf-8' )
end
提取关键词
分词完毕之后,还需要初步筛掉一些对了解文章内容不需要的词,这种词叫做停用词 ,
我随便在网络上面下载了一份,大致能用,在这里下载 。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
def stop_words
File . read ( 'chinese_stop_words.txt' ) . split . sort
end
def cn_filter_stop_words words
( words - stop_words ) . reject do | word |
stop_words . map do | sw |
word . include? ( sw )
end . any?
end
end
对了,分词之前,还需要对文章预处理一下,去掉一些比较杂的东西。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
def cn_tokenize text
out = text . downcase
# Strip all HTML
out = out . gsub ( /<[^<>]+>/ , ' ' )
# Strip all number
out = out . gsub ( /[0-9]+/ , ' ' )
# strip all url
out = out . gsub ( /(http|https):\/\/[^\s]*/ , ' ' )
out = cn_word_split ( out )
out = cn_filter_stop_words ( out )
out . reject do | word |
word . length <= 1
end
end
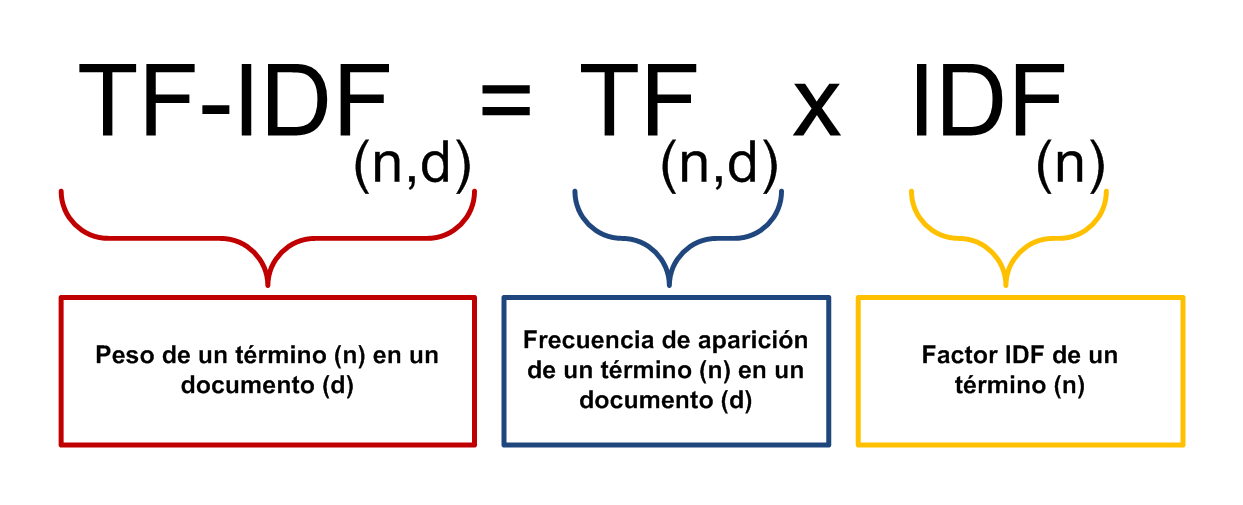
我采用tf-idf 的方式给文章中所有词算好一个权重。
关于tf-idf的介绍,可见这里 。
我采用的是一个叫tf_idf 的Gem,
同时我把文章title,tag等也当做词加入进文章内容中。为了表示title和tag的重要性,
出现在title和tag中的词,相当于出现在文章中的次数为系数k(我选取的是10和5)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
def pre_token item
tw = cn_tokenize ( item . title )
dw = cn_tokenize ( item . desc )
gw = item . taggings . map { | t | t . tag . name }
tw * 10 + gw * 5 + dw
end
require 'tf_idf'
def caculate items
corpus = items . map { | item | pre_token ( item )}
data = TfIdf . new ( corpus ) . tf_idf
end
选择类似的文章
把文章抽象成一个在关键词作为维度的多维空间的向量,然后2篇文章的相似度就是它们之间的夹角。
这种方法叫余弦相似度 。
按照公式 :
实现起来很简单:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
def similars data , d1
data . each_with_index . map do | d2 , i |
same_keys = d1 . keys & d2 . keys
score = same_keys . map { | k | d1 [ k ] * d2 [ k ] } . sum
score /= (
Math . sqrt ( d1 . values . map { | v | v ** 2 } . sum ) *
Math . sqrt ( d2 . values . map { | v | v ** 2 } . sum )
)
[ score , i ]
end . sort . reverse
end
上面函数返回的就是按照相似度排列的item列表了。
我考虑只展示前5个相似度比较高的,如果还是没有,选择相似度最高的2个。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
def filter_similars similars , i
selected = []
similars . each do | score , j |
# escape same item
next if j == i
# max similar
break if selected . length >= 5
# max similar for score too low
break if selected . length >= 2 and score < 0 . 1
selected << [ score , j ]
end
selected
end
结论
稍微调整一下之后,列出来相似文章还是大致靠谱的。关于整体开发过程,还是有一些可以说的。
在调研上面花费了很多时间,走了弯路。这个领域我不熟悉,搜索资料,尝试各种其他方法上面,花费了不少的时间。
比如有一个python专门关于Topic Modeling的库叫gensim ,
我打算用它,不过现在项目主要用ruby,我尝试互相调用,最后还是失败了,还是走回全部ruby的方法。
现在全部流程是批次的,每次有新的文章进来,都需要重新算,一次计算需要消耗我自己rMBP时间100秒左右,
计算开销还是很大的。不过现在网站压力不大,放到后台慢慢算。
关于推荐准确率,瓶颈主要在关键词获取,现在的方案中,分数比较高的词很多还是会不准确,
如果要提升的话,可能要用更多数据输入过滤掉更多的词,或者通过语义分析只提取名词,
不过现在得到的结果还行,优化的问题等真正需要面对的时候再说,先去做其它一些更重要的事情吧。